| |
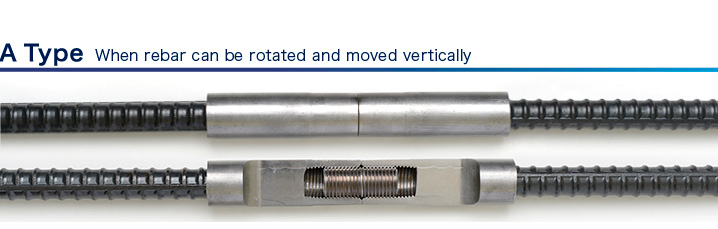
| FD Grip | Used in a Wide Range of Applications, from Large Scale Structures to Railways, and Houses From the Seto Ohashi Bridge to the Yokohama Bay Bridge and Japanfs hallmark high-speed railway system, the Shinkansen. FD Grip mechanical joint for deformed bars have been used extensively in civil engineering and building projects in Japan. FD Grip mechanical joint enable installation by high-strength connection-bolt onsite, through pre-treating both ends of steel bars with sleeves fabricated with NUMEJI joints via a cold-bonding process using a specialized swaging machine. Superior both economically and in terms of workability, FD Grip mechanical joint are easy to install and do not require specially trained workers, making them ideal for large-scale civil engineering and building projects. |
 |
Strength, Workability, Low Cost
FD Grip mechanical joint are stronger than the tensile strength of reinforce rebar itself, and the results of 2 million fatigue tests and low-temperature testing has demonstrated their superior performance. Needless to say, it also help to significantly improve the safety of structures.Discover the Extensive Advantages Offered by FD Grip FD Grip is also easily installed onsite by simply joining with connection bolts and tightening until the prescribed torque is reached. No bulking agent is needed. Installation work can also be easily performed in narrow spaces, congested reinforcement arrangements and in high places. In addition, installation work is not affected by the weather. In this regard, our FD Grip mechanical joint help reduce onsite work, improve efficiency, and are easy to install, each of which helps to reduce costs significantly. |
 |
¡The Building Center of Japan-Performance Standards for Steel Couplers ?Class A ¡Japan Society of Civil Engineering-Steel Coupler Guidelines (2007 Edition) Stand-alone Performance Class SA ¡Demonstrated performance in high-cycle repeated fatigue testing (2 million times) |
 |
FD Grip mechanical joint are structurally best suited for following job site applications. ¡Post-work sites, such as beam bars and slab bars on continuous underground walls, etc. ¡Joining the repetitive placing joint surfaces for roadway floor slab repair work, etc. ¡Sites where future additions to buildings and other structures are planned ¡Cast-in-place sites used in the precast construction methods ¡Mounting inserts, etc., for exterior hardware (on staircases, etc.) ¡Column bars and wall bars in inverted construction for underground structures ¡Post-work sites on temporary openings in beams, floors, and walls, etc. |
 |